

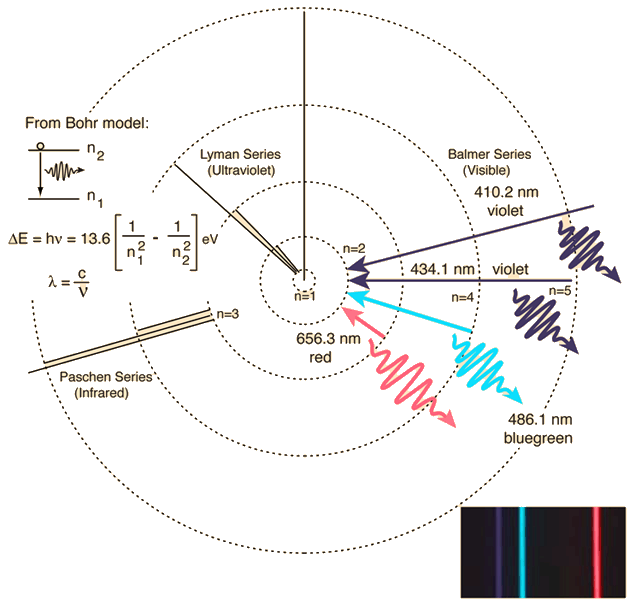
When an electron falls from a higher energy level back to the lower energy level, then radiation of the same frequency (wavelength) is emitted. When an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level in an atom, energy of a characteristic frequency (wavelength) is absorbed. The light emitted by an element when its electrons return to a lower energy state can be viewed as a bright line emission spectrum.ĩ Light Electronic energy is quantized (only certain values of electron energy are possible). This provides information about the relative energies of. When an atom absorbs energy so that its electrons are “boosted” to higher energy levels, the atom is said to be in an EXCITED STATE.ħ Note the same pattern for a given element. When electron transitions take place the energy emitted can be detected and its wavelength measured. The excited atoms emit light of a certain wavelength that corresponds.
#Atomic spectra light energy and electron structure series#
Planck had related the frequency of radiated light to energy change in matter without a model of the atom. Atomic spectra are a series of colored lines emitted by atoms when they are excited. When all electrons are in the lowest possible energy levels, an atom is said to be in its GROUND STATE. The frequency of the emitted photon, its color, depends on the magnitude of the jump. of energy possessed by a photon depends on the color of the light.ĥ What does this have to do with electron arrangement in atoms? light interacted with the electrons in an atom to produce spectral lines. Each photon of light has a particular amount of energy (a quantum). Consider the energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom according to the Bohr. We can describe light as composed of particles, or PHOTONS. Presentation on theme: "Light, Photon Energies, and Atomic Spectra"- Presentation transcript:ġ Light, Photon Energies, and Atomic SpectraĮlectromagnetic radiation (radiant energy) is characterized by its: wavelength (color): λ (Greek letter lambda) frequency (energy): ν (Greek letter nu)ģ Waves Wavelength = distance between successive “crests”įrequency = the # of crests passing a given point per secondĤ Light When sunlight or white light is passed through a prism, it gives the continuous spectrum observed in a rainbow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
